Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)#
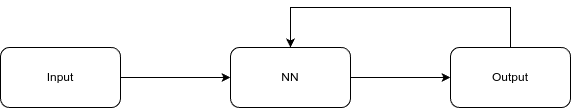
RNNs were a simple modification to feedforward NNs where output was fed back into the network. This is similar to skip connections in ResNet but in opposite direction.
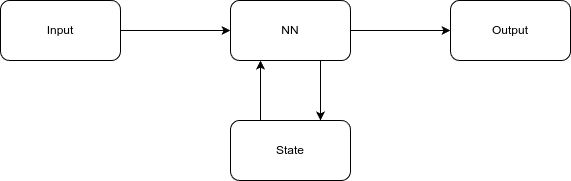
Later it was realised that adding a state can provide more context to the network. The state shares some information from the previous time step to the current time step.
A simple RNN can be represented as
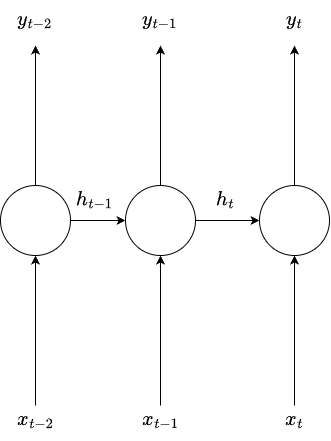
The output is
\(y_t = \phi(W_y h_t + c)\)
where, \(h_t = f(x_t, h_{t-1})\)
Precisely,
\(h_t = \phi(W_x x_t + W_h h_{t-1} + b)\)
A nice paper on RNN: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2014/file/a14ac55a4f27472c5d894ec1c3c743d2-Paper.pdf
Input output types#
The output and inputs of an RNN can be of different lengths, facilitating different tasks.
1. Sequence to Sequence (Seq2Seq) Models#
These are mainly used for time series data and machine translation.
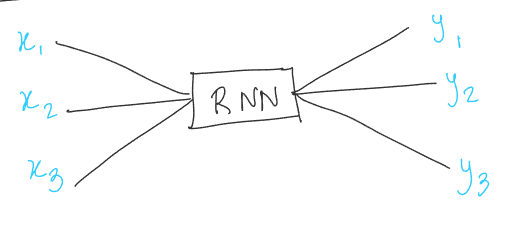
2. Sequence to vector models#
When output is of a fixed length. Such as sentiment analysis or text classification.
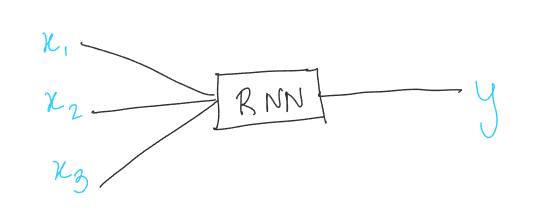
3. Vector to sequence models#
When input is of fixed length and output is of variable length. Such as image captioning.
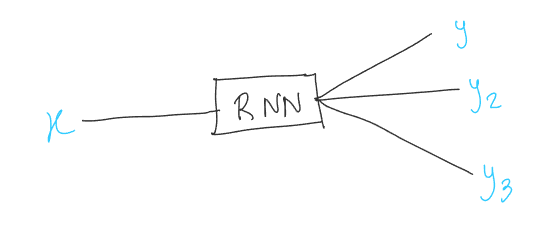
4. Encoder-Decoder models#
These are used for tasks where input and output are of different lengths. The encoder encodes the input and the decoder decodes it.
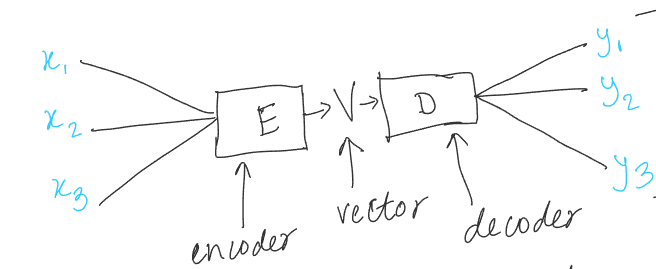
Further Reading#
Modification to RNNs#
Later, the state was modified to become more complicated. Different types of RNNs use different ways to update the state, for example, Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU).The state is a cell, with gates like input, forgot and output. The input gate decides what information to store in the cell, the forget gate decides what information to throw away from the cell and the output gate decides what information to output from the cell.
Long Short Term Memory (LSTM)#
To account for context LTSM uses gates. The cell state is used to define the long term memory and the hidden state is used to define the short term memory. Both states are updated using the forget gate, input gate and output gate.
Long short term memory#
later
